This instruction show you guide on how to solve Kubota V3800 engine high fuel consumption trouble.If you need know more case of Kubota V3800 enigne,please check Kubota Trouble Repair.
Related Contents:
Takeuchi Excavator Workshop EPC+Service Manual 2018 PDF Files
2022 Kubota Takeuchi Diagmaster v22.08.01 v4.1.2 Software Free Download
Kubota EPC Spare Parts Catalogue 2021.06 Download
Possible Causes:
Reduced engine performance is detected and the fuel consumption is higher for this reason.
1.The engine performance is reduced and the fuel consumption is higher for this reason
Reduced engine performance is not detected but the fuel consumption is higher.
Usage habits of the user or use of non-standard parts
- Not the standard specification
– Tires, wheels
– Intake / exhaust system parts
- Used for a long time under poor fuel consumption conditions
– Engine used for a long time under a high load
– Long idling time
- Frequently used under driving conditions with a large injection quantity
– Low mileage for each drive (frequently used before the engine has warmed up)
- Faulty maintenance
– Engine oil (dirt)
– Air filter, fuel filter (dirt, clogging)
– Radiator clogging
2.Powertrain malfunctions not involving the engine
- Large driving resistance
– Large resistance for actuation
– Tire air pressure
– Brake drag
- Clutch slipping
3.Fuel pump operation fault.
4.Engine fault
- Low compression pressure.
- Engine internal fault
- Valve clearance fault
- Valve timing fault
- Engine oil viscosity fault
5.Control system
- Damage to the pulsar gear of the crankshaft position sensor
- Air gap of the crankshaft position sensor is large
- SCV operation fault
6.Intake system
- Air cleaner clogging
- Leak from the intake system parts
- Turbocharger operation fault
7.Fuel system
- Supply pump learning has not been performed
- Fuel quality
- Fuel pressure limiter fault
- Fuel line clogging, leak
8.CRS (including related parts)
- Output system (supply pump and injector)
- Input system (sensors) *A cause for larger injection quantity
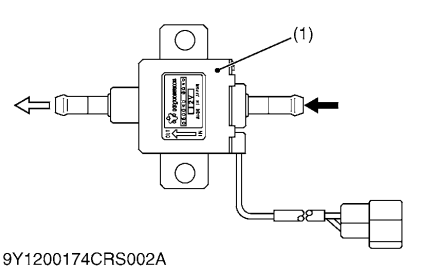
1.Check the Fuel Pump Operation
Turn the key switch ON and check that the fuel pump is operating.
Factory specification:Operates when the key switch is turned ON.
OK Go to “2. Check the DTC”.
NG Check in accordance with “6.[2] FUEL SYSTEM INSPECTION PROCEDURE – 5. Check the Fuel Pump”. (Refer to page 1-S289)
2.Check the DTC
Turn the key switch ON and check the DTC.
Factory specification:No DTC is output.2
OK Go to “3. Comparison of Fuel Economy”.
NG Check in accordance with the troubleshooting procedures for each DTC.
3.Comparison of Fuel Economy
Compare with a normal device working under the same operating conditions and measure the amount of consumed fuel(amount left in the tank).
OK Use a specific example to explain and make the user understand that under some operating conditions the fuel consumption will increase and that the machine is not malfunctioning.
NG Go to “4. Check the Engine and Machine Condition”.
4.Check the Engine and Machine Condition
Check for the usage habits of the user or use of non-standard parts.
- Use of non-standard parts such as tires, wheels and intake / exhaust system parts
- Used under poor fuel consumption conditions
– Engine used for a long time under a high load
– Long idling time
- Faulty maintenance
– Engine oil level and dirt
– Air filter, fuel filter dirt and clogging
– Radiator clogging
OK Go to “Check for malfunctions in the powertrain”.
NG Give guidance to the user
Check for malfunctions in the powertrain.
- Check the driving resistance
– Is a large resistance required for actuation?
– Is the tire air pressure correct?
– Is there brake drag?
OK Go to “5. Check the Fuel System”.
NG Adjust or repair the malfunction.
5.Check the Fuel System
Check in accordance with “6.[2] FUEL SYSTEM INSPECTION PROCEDURE”. (Refer to page 1-S287)
(Reference) Pay attention particularly to the following two points:
- Service fuel (for summer / winter seasons, and cold region)
- Fuel leak from the fuel line
OK Go to “6. Check the Intake System”.
NG Repair or replace the malfunctioning component.
6.Check the Intake System
1Check in accordance with “6.[1] AIR INTAKE SYSTEM INSPECTION PROCEDURE”. (Refer to page 1-S286) (Reference)
Pay attention particularly to the following point:
- Intake air leak
OK Go to “7. Check the Coolant Temperature Increase Rate”.
NG Repair or replace the malfunctioning component.
7.Check the Coolant Temperature Increase Rate
Check the speed of the coolant temperature increase on the coolant temperature gauge in the instrument panel (compared with a normal device)
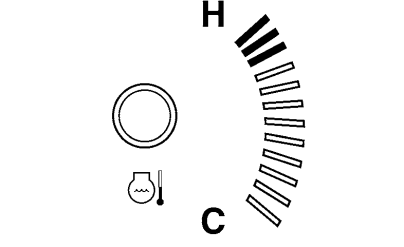
OK Go to “8. Check the Crankshaft Position Sensor”.
NG Check and repair the cooling system.
8.Check the Crankshaft Position Sensor
Refer to DTC P0335 and P0336, and implement checking of the crankshaft position sensor.
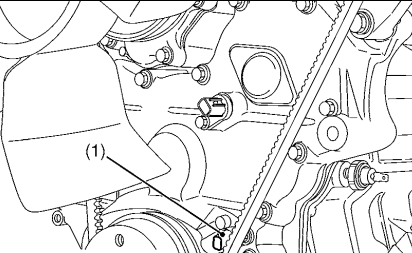
OK Go to “9. Check the Camshaft Position Sensor”.
NG Repair and replacement of the crankshaft position sensor-related parts.
9.Check the Camshaft Position Sensor
Refer to DTC P0340 and P0341, and implement checking of the camshaft position sensor.
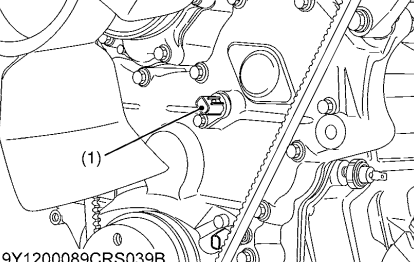
OK Go to “10. Check the Rail Pressure Sensor And Supply Pump”.
NG Repair and replacement of camshaft position sensor-related parts.
10.Check the Data Related to Pressure Control
Measure the “Target rail pressure” and “Actual rail pressure” when accelerator is operated as indicated below using the diagnosis tool data monitor function.
Factory specification
The “Actual rail pressure” always follow to the “Target rail pressure”.
1.When idling:40 to 50 MPa (410 to 500 kgf/cm2, 5800 to 7200 psi)
2.Accelerator opening 0 → 100 % (During acceleration):
Maximum value 95.0 to 130 MPa (969 to 1320 kgf/cm2,13800 to 18800 psi)
3.No-load maximum speed: 95.0 to 115 MPa (969 to 1170 kgf/cm2, 13800 to 16600 psi)
4.The numerical value is stable under normal operating andthe target value corresponds with actual pressure value.
OK Go to “11. Check the Injector (Including the Pipes, etc.)”
NG (Check the trouble related to pressure
perform diagnosis for the ECU, wiring harness and sensor, and repair or replace the required parts.
NOTE
- Some diagnosis items above may be mentioned twice.
11.Check the Injector (Including the Pipes, etc.).
Perform the diagnosis tool active test (stopping the injector injection by cylinder) and check the injector performance.
Factory specification
Engine vibration and noise are increased and the rotation speed is reduced when the injection for the corresponding cylinder is stopped.
The same results must be attained from all the cylinders.
OK Go to “12. Check the Engine”.
NG Check and repair faulty parts including the high pressure line of the defective cylinder.
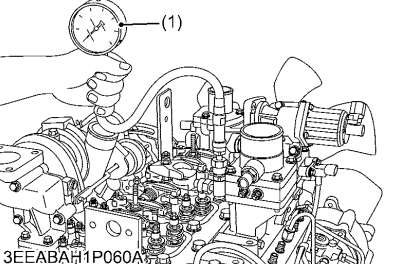
12.Check the Engine
Check the compression pressure, valve clearance, valve timing, the inside of the engine and engine oil viscosity.
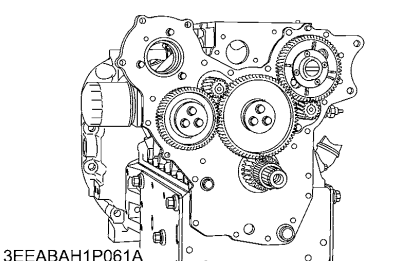
Check the timing gear.
Check the turbocharger.
OK Normal.
NG Repair or replace the related parts